Heat exchangers play a crucial role in industries where heat transfer between two fluids is essential. Whether in power plants, chemical processing, HVAC systems, or oil refineries, these devices ensure energy efficiency and process optimization. To standardize their design and performance, the Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association (TEMA) has classified shell-and-tube heat exchangers into specific types based on their mechanical and thermal design.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two or more fluids without mixing them. It can be used to heat, cool, condense, or evaporate fluids depending on the application.
- Cooling engine oil with water in automobiles
- Condensing steam in power generation
- Preheating crude oil in refineries
Understanding TEMA Standards
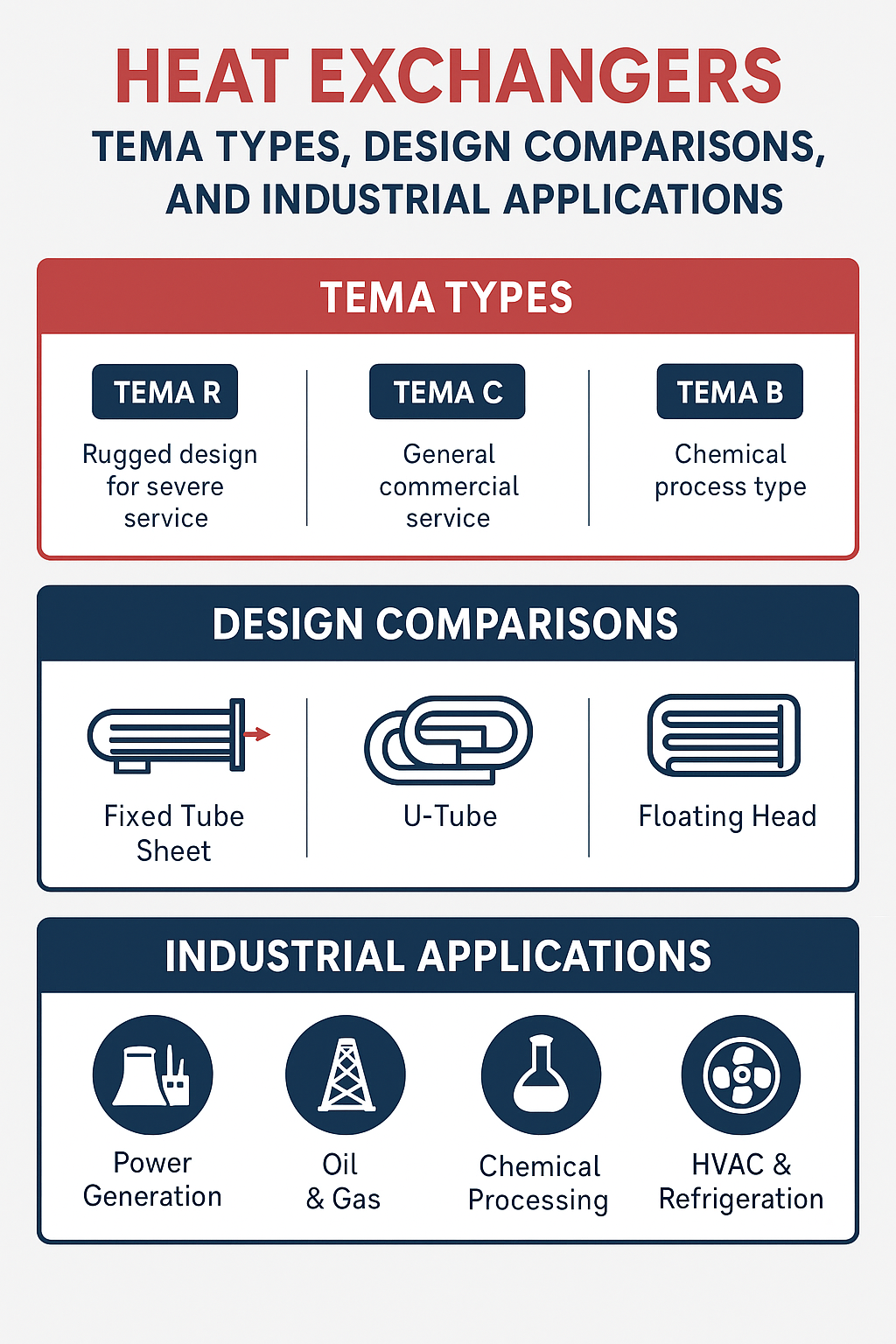
TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association) sets global standards for the mechanical design, fabrication, and testing of shell-and-tube heat exchangers. It ensures uniformity, safety, and performance across various industrial applications.
| TEMA Class | Description | Application Industry |
|---|---|---|
| TEMA R | Rugged design for severe service | Refinery, petroleum, and heavy industries |
| TEMA C | General commercial service | Chemical processing, HVAC, food industries |
| TEMA B | Chemical process type | Moderate operating conditions |
TEMA Type Designations
Each heat exchanger type is identified by a three-letter code, where each letter represents a specific part:
- Front-end head type: A, B, C, N
- Shell type: E, F, G, H, J, K, X
- Rear-end head type: L, M, N, P, S, T, U
Common TEMA Configurations
| TEMA Type | Configuration Name | Description / Features |
|---|---|---|
| AES | Fixed tube sheet exchanger | Simplest and most economical |
| AET | Removable tube bundle | Easy cleaning and maintenance |
| BEU | U-tube design | Handles thermal expansion easily |
| BEM | Floating head exchanger | Suitable for high-temperature differentials |
| CFU | Split flow shell | Enhanced performance and lower pressure drop |
Comparison of TEMA Heat Exchanger Types
| Feature | Fixed Tube Sheet (AES) | U-Tube (BEU) | Floating Head (BEM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Cleaning (Shell Side) | Difficult | Moderate | Easy |
| Thermal Expansion Handling | Poor | Excellent | Excellent |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Condensers, coolers | Process heaters | Refineries, power plants |
Usage and Applications of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are essential across industries for efficient thermal energy transfer. Below are some major sectors and applications:
1. Power Generation
- Steam condensers and feedwater heaters
- Boiler economizers
- Turbine intercoolers
2. Oil & Gas
- Crude oil preheaters
- Gas coolers and condensers
- Heat recovery systems
3. Chemical Processing
- Reactor cooling
- Distillation column condensers and reboilers
4. HVAC & Refrigeration
- Air conditioning evaporators
- Chillers and condensers
5. Food & Beverage
- Pasteurization systems
- Hot water heating and cooling systems
Advantages of TEMA Standard Heat Exchangers
- Uniform design standards and easy interchangeability
- Proven reliability and durability under varying conditions
- Flexibility for maintenance and cleaning
- Customizable for different industrial processes
Key Factors When Selecting a TEMA Heat Exchanger
- Operating Pressure and Temperature
- Fluid Type (Corrosive, Non-Corrosive, Viscous, etc.)
- Maintenance Requirements
- Thermal Expansion Considerations
- Installation Space and Cost
Conclusion
Understanding TEMA types of heat exchangers helps in selecting the right configuration for your industrial process. Whether you need a simple fixed tube design or a flexible floating head unit, following TEMA standards ensures optimal performance, safety, and reliability in heat transfer operations.
FAQs on TEMA Heat Exchangers
What is the purpose of TEMA classification?
TEMA classification ensures uniform mechanical design, fabrication, and testing standards for shell-and-tube heat exchangers used worldwide.
Which TEMA type is best for high-temperature applications?
The floating head (BEM) and U-tube (BEU) types are ideal as they handle thermal expansion efficiently.
What industries use TEMA heat exchangers most?
Oil & gas, power generation, petrochemical, HVAC, and food processing industries commonly use TEMA-standard exchangers.
What’s the difference between TEMA R, C, and B?
TEMA R is designed for refinery and heavy-duty services, TEMA C for general commercial use, and TEMA B for chemical process industries.